Storage Facility Types
WHAT IS RECHARGE?
Direct recharge is the process of flooding an area and allowing water to percolate down through the soil, replenishing underground aquifers. In the future, the recharged water can be pumped out with recovery wells for use in meeting demand. The Arizona Water Banking Authority (AWBA) participates in direct recharge by partnering with operators of recharge projects to store excess Central Arizona Project (CAP) supplies at those facilities.
Indirect recharge (or in-lieu recharge) is the process of using renewable surface water supplies instead of groundwater to irrigate. The reduction in groundwater pumping results in groundwater that will remain in the aquifer and is referred to as "groundwater savings." The AWBA participates in indirect recharge with the agricultural community using CAP water as the alternative surface water supply.
Long-term storage credits are accrued by the AWBA through permitted facilities that store water either through direct recharge or indirect recharge. A credit is accrued for each acre-foot of water that is stored (after losses) minus the 5% cut to the aquifer.
STORAGE FACILITY TYPES
The AWBA delivers water for storage at both Underground Storage Facilities (USF) and Groundwater Savings Facilities (GSF).
 |
 |
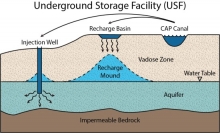
An Underground Storage Facility is a facility that physically stores water in the aquifer through direct recharge. The most common type of recharge project uses infiltration (spreading) basins in which water is spread out over a large surface area and water infiltrates or seeps into the alluvial material eventually reaching the aquifer. These areas are typically located adjacent to stream channels where infiltration rates are high due to the porous nature of the soils. Another type of recharge project involves the use of injection (recharge) wells where water is forced directly into the aquifer through the borehole of the well. This recharge method is less common than infiltration basins because of its higher operational expense. Both infiltration basins and injection wells are categorized as Constructed USFs since they use some type of constructed device to operate.
Another type of USF, a Managed USF allows for water to be discharged to a naturally water-transmissive area such as a streambed, where water can percolate into the aquifer without the assistance of a constructed device.
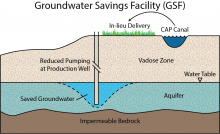
A Groundwater Savings Facility is an indirect recharge facility that uses surface water (CAP water) instead of pumped groundwater. The AWBA partners with an entity (typically an irrigation district) that would have otherwise pumped groundwater and provides CAP water in-lieu of the pumped groundwater. The AWBA then receives long-term storage credits for the groundwater not pumped.