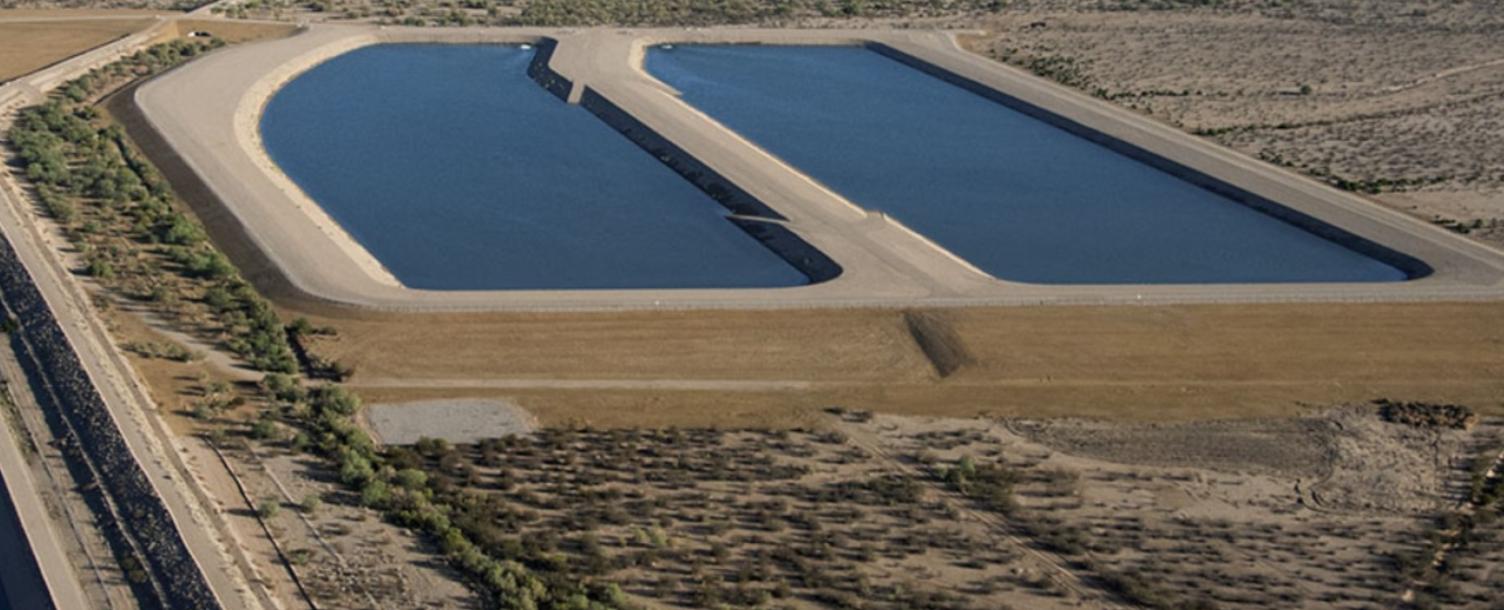
The Arizona Water Banking Authority
The Arizona Water Banking Authority (AWBA; Water Bank) was established in 1996 to store the unused portion of Arizona’s annual Colorado River entitlement in Central and Southern Arizona. The AWBA stores water in underground aquifers to earn long-term storage credits (LTSCs). These credits can be recovered (pumped) during a shortage to provide back-up water supplies (known as "firming") for Arizona water users.
Through 2023, the AWBA has accrued 4,380,000 acre-feet of LTSCs: 3,770,000 acre-feet for Arizona uses and 613,846 acre-feet on behalf of the State of Nevada. The AWBA firms water supplies for Central Arizona Project municipal and industrial subcontract holders and communities along the Colorado River. As the agent for the State, the AWBA is responsible for meeting the State's Tribal firming obligations under the Arizona Water Settlements Act of 2004. The AWBA also assists with meeting the State's water management objectives under the Groundwater Code and provides the mechanism for interstate water banking with the other Lower Basin States. By storing water, the AWBA helps to ensure long-term water supplies for Arizona and neighboring states.
Announcements

2023 Annual Report
The AWBA is pleased to share its 2023 Annual Report. The Annual Report details the AWBA’s activities for calendar year 2023 and the progress made on achieving its goals and obligations including commitments made in support of Arizona’s plan for implementing the Lower Basin Drought Contingency Plan

Comments from CAP M&I Subcontractors on the 2023 Draft Annual Report.
Comments received during public review of AWBA 2023 Annual Report.

ADWR Water Awareness Month Festival
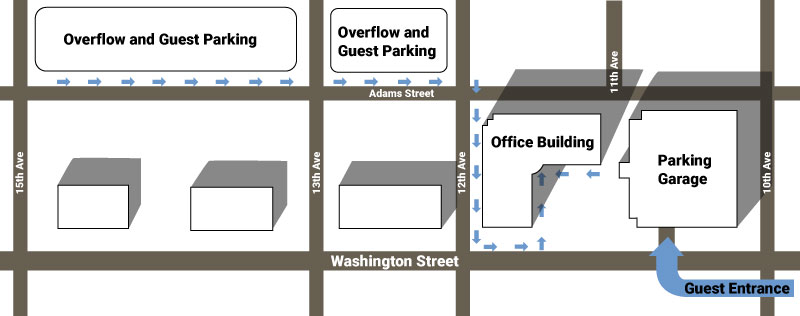
On Saturday, April 6th, the Arizona Department of Water Resources held a Water Awareness Month festival at the Wesley Bolin Plaza in Phoenix (1700 W Washington St, Phoenix, AZ 85007). The Arizona Water Banking Authority tabled at the event and greatly enjoyed the opportunity to meet with members of
NEXT QUARTERLY MEETING
The next quarterly meeting of the Arizona Water Banking Authority Commission has been tentatively scheduled for Wednesday, September 11, 2024 - 10:00 a.m. - 12:00 p.m.
This meeting will be held both in-person and via webinar with login details posted 24 hours prior to the meeting.
Pursuant to A.R.S. § 38-431.02(A)(1), all public notices of meetings of the AWBA Commission and any of its subcommittees will be physically posted at the Arizona Department of Water Resources, 1110 W. Washington St., Phoenix, Arizona, near the elevators on the first floor, which is open to the public Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m., except legal holidays. AWBA Commission meetings will also be electronically posted to this website under Meetings.